⚖️Can Old Laws Protect New Tech and Us?
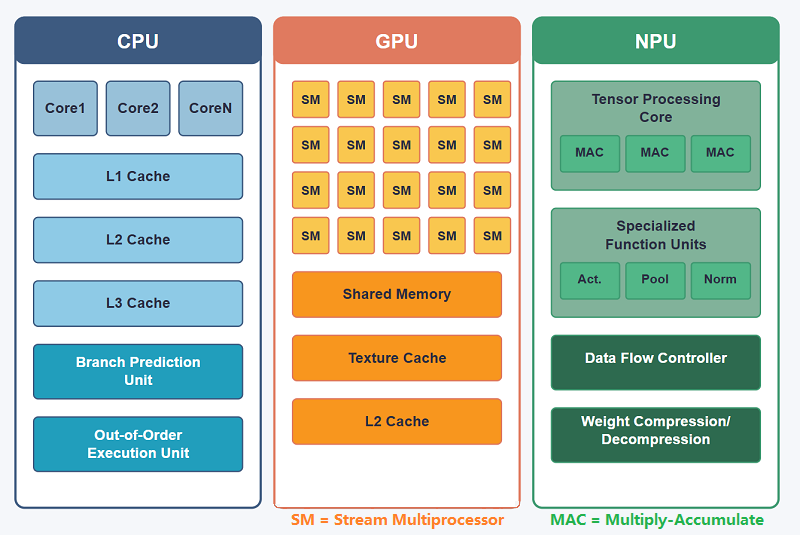
What NPUs Are and Why They Matter
Happy New Year, team. We’re back with renewed energy and a sharp focus on researching and delivering the most thoughtful, data-driven AI and tech insights, word for word. Today’s issue breaks down how NPUs are changing the AI hardware game, why inference, not training, is shaping 2026, and whether outdated laws and a rigid judicial system can realistically protect citizens from powerful, fast-moving tech giants. Let’s dive in and, as always, stay curious.
What NPUs Are and Why They Matter
🧰 AI Tools - Inference NPUs
The Business of NPUs and the Shift to Inference
🛠️ AI Jobs Corner
Can Old Laws Protect New Tech and Us?
📘Learning Corner
Subscribe today and get 60% off for a year, free access to our 1,500+ AI tools database, and a complimentary 30-minute personalized consulting session to help you supercharge your AI strategy. Act now as it expires in 3 days…
📰 AI News and Trends
Samsung Electronics to expand the number of mobile devices running AI features powered by Google’s Gemini from ~400 million to 800 million units this year, including smartphones and tablets.
OpenAI reportedly prepares audio AI upgrades for first ChatGPT hardware
xAI’s chatbot Grok posted a series of sexualized images of minors on X. Grok's account was later attributed to the BS of “lapses in safeguards.”
Google Gemini's new feature called “Guided Learning” is a true game changer. Basically, a private teacher at your disposal who walks you through any topic until you totally understand it.
Other Tech News
Apple has reportedly cut Vision Pro headset production and marketing spend by more than 95% after demand fell well short of expectations.
Tech executives sold more than $16 billion worth of shares in 2025 as AI-driven rallies pushed stock prices to record highs
US spot crypto ETFs crossed $2 trillion in cumulative trading volume on January 2, doubling in half the time
Top social media alternatives to Instagram and TikTok.
Can Old Laws Protect New Tech and Us?
As 2026 approaches, courts are bracing for a wave of high-stakes lawsuits that will test the application of decades-old laws to modern technology, particularly AI, algorithms, and digital platforms. Key cases span AI-driven price-setting software accused of enabling illegal collusion, copyright battles over training AI models on code and creative works, privacy suits applying 1960s wiretapping laws to online tracking tools, and massive litigation against social media and gaming companies over alleged addiction and mental-health harms to minors. With thousands of cases consolidated nationwide and potential statutory penalties reaching billions of dollars, these disputes won’t just decide winners and losers; they will define the legal rules of the digital economy, clarifying where innovation ends and liability begins when algorithms, platforms, and data cross the line.
The real question is whether laws, and the lawyers who interpret them, are capable of keeping pace with rapid technological change. Can a legal system built on slow processes, rigid frameworks, and legacy thinking truly adapt to regulate AI, data, and digital platforms in a way that protects users, minors, and less-informed citizens without suffocating innovation?
If the law cannot evolve beyond red tape and narrow interpretations, it risks either failing to prevent harm, such as data misuse and behavioral manipulation, or overcorrecting in ways that discourage entrepreneurs from building the next generation of technology.
🛠️ AI Jobs Corner
Apply Today - Open Positions.
First-Line Supervisors of Productions and Operating Workers
Computer and Information Systems Managers
What NPUs Are and Why They Matter
Neural Processing Units (NPUs) are specialized chips built specifically to run AI models efficiently, especially during inference, the phase where trained models are actually used. Unlike GPUs, which are general-purpose and power-hungry, NPUs are optimized for neural-network math like matrix multiplication and tensor operations. The result is 2–10× better performance per watt for common AI workloads, according to industry benchmarks. This efficiency matters because inference already accounts for ~60–70% of total AI compute costs in production systems, and that share is growing fast as AI moves into phones, cars, cameras, and enterprise apps. In short: GPUs train AI, NPUs run AI at scale cheaply, quietly, and everywhere.
📘Learning Corner
Inference
For Architecture & Hardware: Synopsys Blog offers excellent technical breakdowns of AI chip design, including why NPUs require different memory and processing architectures than traditional chips.
For Benchmarks & Comparative Performance: SemiEngineering and Ars Technica provide deep-dive analysis on real-world performance. You can find reports comparing NPU power efficiency (TOPS/W) against GPUs.
For FuriosaAI Specifics: The FuriosaAI Technical Whitepaper (often found under their “RNGD” product page) explains their Tensor Contraction Processor (TCP) architecture, which is their specific way of making NPUs faster for large models.
The Business of NPUs and the Shift to Inference
The AI chip market is entering its next phase: inference-first economics. Training large models still favors Nvidia’s GPUs, but inference is where volume lives, billions of daily requests, tight latency budgets, and exploding energy costs.
This is why companies are racing to build their own silicon. Google runs AI on TPUs, Amazon deploys Inferentia and Trainium on AWS, and Meta designs in-house chips to power feeds for billions of users. Startups like FuriosaAI and Groq are betting that faster, cheaper inference will unlock real margins. The stakes are high: inference spending is projected to surpass training spending by 2027, and whoever controls efficient inference controls the economics of AI deployment. NVIDIA remains dominant, but the market is fragmenting, and custom NPUs are becoming strategic infrastructure, not just hardware.
The $800 Million "No": FuriosaAI rejected a massive acquisition offer from Meta in 2025. This shows that the value isn't just in the hardware, but in staying independent in a market hungry for Nvidia alternatives.
🧰 AI Tools of The Day
Inference NPUs
Google Cloud TPU – Rent Tensor Processing Units for AI training and inference
AWS Inferentia / EC2 Inf1 & Inf2 – Rent AWS’s NPU-class inference chips via EC2
GMI Cloud – Specialized cloud platform for on-demand AI inference compute
AWS Trainium / SageMaker – Though focused on training, you can access optimized AI inference with AWS infrastructure